News
Prof. Zonghoon Lee’s Atomic-Scale Electron Microscopy Lab
Prof. Zonghoon Lee’s Atomic-Scale Electron Microscopy Lab

2D layered materials, such as graphene and hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) have attracted significant attention for potential applications in 2D materials due to their excellent thermal and mechanical properties. Moreover, hBN, also known as “white graphene” has already proved itself to be a good substrate for graphene as they both have a similar lattice constants.
While defects in graphene have extensively been investigated, the mechanisms for defect formation in a h-BN sheet is still largely unclear due to the much more varied and complex structures of h-BN. Indeed, its hexagonal 2D lattice is occupied by two elements.
On June 28, a team of UNIST and Sejong University researchers announced they have observed triangular hole growth processes in monolayers of hBN for the first time in history. In this study, the growth of triangular holes in hBN monolayers was monitored over time via Atomic Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (ARTEM) imaging.
This study is a collaboration among scientists, including Prof. Zonghoon Lee (Department of Energy Engineering) and Prof. Suklyun Hong (Graphene Research Institute and Department of Physics) at Sejong University.
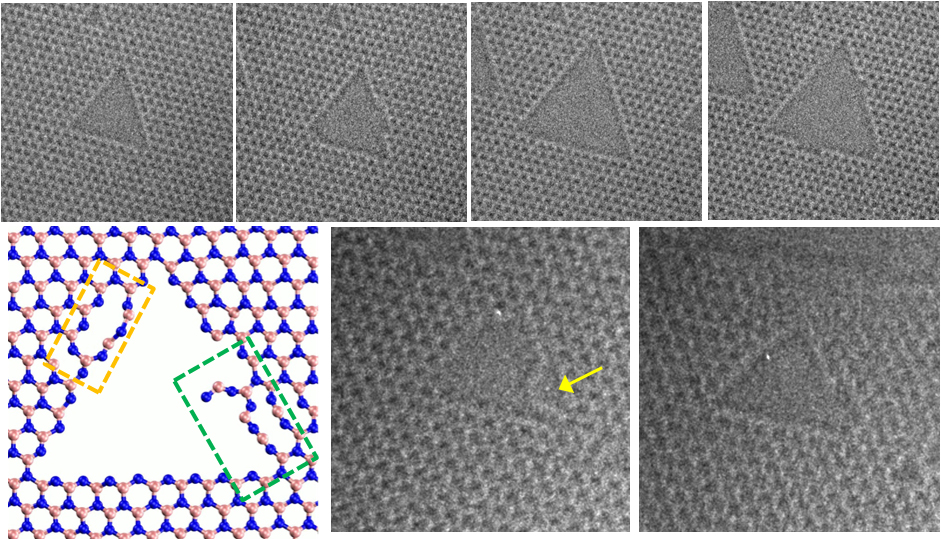
Through a series of TEM images that were supported by DFT calculations and MD stimulations, the team discovered that these holes apper to be initiated by the formation of a vacancy of boron and grow in a manner that retains an overall triangular shape.
This article has been made straight to the front page of the July 2015 issue of the Royal Society of Chemistry Journal Nanoscale, a high impact journal publishing experiemental and theoretical work across the breadth of nanoscience and nanotechnology.
Moreover, it has been selected to be featured in 2015 Hot Papers in Nanoscale, an on-going web collection showcasing all of the Hot Nanoscale articles published in 2015, as recommended by referees.
“This new technology will provide a promising direction for the synthesis and fabrication of future two-dimensional electronics,” says Prof. Lee.
This work has been supported by the Nano Material Technology Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and Priority Research Center Program through NRF funded by the Ministry of Education (MOE), and the Office of Naval Research and the Institute for Basic Science (the IBS-R019-D1).
Journal Reference:
Gyeong Hee Ryu, Hyo Ju Park, Junga Ryou, Jinwoo Park, Jongyeong Lee, Gwangwoo Kim, Hyeon Suk Shin, Christopher W. Bielawski, Rodney S. Ruoff, Suklyun Hong, and Zonghoon Lee, “Atomic-scale Dynamics of Triangular Hole Growth in Monolayer Hexagonal Boron Nitride under Electron Irradiation.” Nanoscale (Royal Society of Chemistry), 2015, 7, 10600-10605.